Whether you’re a seasoned Google user or new to the Googling game, it’s important to understand how to use the platform to your advantage.
Even if you don’t consider yourself web-savvy, you’ve probably done a Google search at some point! Checking the weather? Need to find pizza near you ASAP? Google is your info-finding BFF If you’re a business owner, you will also benefit from understanding how people use Google to search the web because it’s a major way that people may find your business.
Let’s talk about how to get the best, fastest results for all your Google search queries.
Who should learn how to improve Google search results?
New Google Users
Pre-Google generations, or regular users that are just beginning to use the platform benefit from understanding basic tips and strategies to improve their Google results page when searching for information or an answer to their question.
Business Owners
Business owners can largely increase their organic reach by improving how their business shows up and ranks in users’ results pages. If you can think like a user while writing content, your website is much more likely to perform better on various search engine results pages.
Seasoned Users
Have you been using Google for years? Turns out there are a lot of features and shortcuts that the average user doesn’t know about or take advantage of. It never hurts to learn something new.
Students
As a former English teacher, I’ve found that students need to learn how to use Google to research efficiently. Teachers might automatically assume that since students grow up with this technology, they know how to use it well. I know I did!
Unfortunately during research units, countless students would come up to me feeling lost because they couldn’t find sources. They thought they needed to change research topics, when in reality they just needed to make adjustments in HOW they search.
Basic Google SERP Strategies
SERP stands for Search Engine Results Page. It’s the results page that comes up after you complete a search query on Google. Below are some common user errors and tips to enhance your Google SERP.
You don’t need to include article words (most of the time)
Article words such as a/an and the don’t help the search engine because these words aren’t specific and they’re everywhere. When Google’s algorithm is combing through information, words like a/an are on virtually every page, so it doesn’t give you better results.
Unless an article word is in the title of what you’re searching for, (like The Supremes music group) you don’t need to include it.
For example, the Google SERP is the same for both of these search phrases: supreme court and the supreme court.
It’s a minor change, but this tip can save you a lot of time and typing!
You don’t need to obsess over grammar and capitalization
Remember that “talking” to a computer algorithm is a lot different than communicating with actual people; Google is not judging your grammar when you type in a search query. In fact, the Google algorithm has learned a lot of common grammar and typing errors and takes them into consideration while you search.
You might’ve noticed Google accounting for errors when there is a bold blue message at the top of the SERP saying showing results for or did you mean with the correct spelling after it. Unless you completely butcher the spelling, Google can probably figure out what you mean.
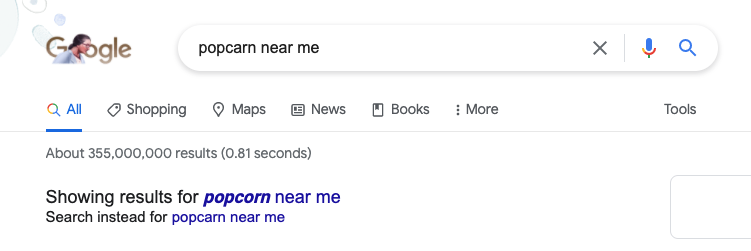
Capitalization does not disrupt your search at all. Unless it bugs you, don’t worry about having perfect capitalization for proper nouns when searching. Google search results are not case sensitive.
Switch up your search terms and phrases
Not finding what you’re looking for? Switch up your word choice. Essentially, Google gives the best results by finding the sites with the most commonly searched words and phrases (they also take other factors into account, but we’ll get into that at another point in time ).
The website pages with the most commonly used keywords and phrases have a higher SEO rank, meaning these keywords and phrases rank on the first couple pages of Google, or even appear at the top of the page. SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. If a website has good SEO, it ranks better in Google. We’ve even made an easy to follow SEO checklist for you if you’re writing web content for your business’ website!
Related: What is SEO? The Ultimate 2020 Guide to Search Engine Optimization →
Avoid using regional terms for search queries
Say you’re looking for a specific soda, but you’re from an area that calls it “pop.” You will struggle to find information if you’re using a specific regional term while searching for it. Try switching out the word to a term that most users would search. Google even has a tool to help you find this information, called Google Trends.
Avoid hyper-specific, long phrases
Sometimes you can hinder your own search experience with a phrase that is way too specific or long. Try to think in general terms and avoid too many adjectives and words.
Over five words in your search query (also called a long-tail keyword) is pushing it. You’ll end up with a lot of information, but it won’t include all of the words in your search, (it may find pages that have 3 or 4 of them) so it won’t find noteworthy results.
For example, searching purple fuzzy v-neck sweater with glitter and rainbows will not find that exact item for you. Your SERP page might find sites that include maybe 4 to 5 of those words.
When you add more words to the search, you’re actually casting an even bigger net, not getting more specific results. Because it might find pages with a couple words out of the long phrase search query, it might start showing items like glitter rainbow toys or purple fuzzy pillows–neither is relevant.
Instead of being so specific, look at the terms that aren’t showing up and pick a more generic word that might get you closer to what you’re searching for. For this example, I would search purple sweater with graphic to yield more realistic results to browse through.
Add more description
Sometimes you might have the opposite issue happen, and have overwhelming, vague results. This is where adding a descriptor or two will help your Google SERP. Think of words that describe the item or information you’re looking for. Words that explain appearance, size, location, time period, etc. will narrow down your search.
Think of synonyms and more descriptive words
Switching your word choice has a dramatic effect on the results page. Say you were shopping online for a new couch. Some word options to add or switch could be sectional, leather, or modern instead of just the generic search term new couch. These former terms would produce specific pages with these keywords that are more detailed and comprehensive, rather than a basic overview.
How to search when you can’t think of what to type
Google has a handy autofill feature that guesses your search query based on the beginning words you type in. For example, when I type in how to, Google shows ten current popular searches beginning with those words below the search bar. If you have a topic you’re interested in but you’re not sure what else to add, this is another way to specify your search and see what other users are searching for.
Other ways to find information fast
With Google moving more toward zero-click searches, it’s easier than ever for you to find the information you’re looking for without having to sort through search results. Below are some basic quick search tips to help you find what you need.
Looking up the weather forecast ☀️
If your location setting is on, type weather for a full weekly forecast of your area. If you don’t have your location on, type weather, then your city, town, or zip code.
Dictionary
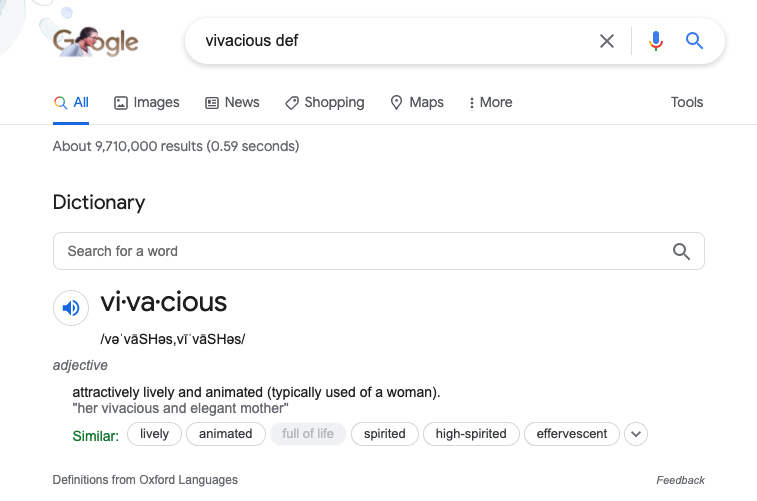
Type definition + any word (I sometimes just write def). Not only will Google give you the definition, but you can click the speaker for an audio pronunciation. There’s even a learn to pronounce feature that appears after you’ve listened to the pronunciation!
Unit conversions
Type in any conversion, such as 5 kilometers in miles and Google will convert it for you.
Sports
Enter the name of your team to see a schedule, scores, and more!
Action verb + whatever you’re looking for
Search queries like order Pizza Hut or register to vote will take you to a results page with an easy-to-find answer.
Want to avoid a specific website?
If you’ve been researching and a certain unhelpful site keeps coming up, put a minus sign, the website name, and another minus sign after the site name, along with your other search terms, for Google to take it off the SERP.
So if I wanted to avoid Wikipedia when researching The Beatles, I would type:
The Beatles -Wikipedia-

How to use Google for Research
Feeling overwhelmed conducting Google research? Whether you’re writing your own SEO blogs, writing a research paper, or searching for a service or product, using Google efficiently can prevent you from spending hours looking for source material. Instead, you can focus those hours on using the best information for your task. Below are some tips and tools to help you find the best sources using Google.
Use .gov, .edu , and .org domain name extensions to find credible sources
This is an easy trick when you’re looking for articles that are reliable and have enough information. A .com website isn’t necessarily unreliable, but other types of websites make it a little easier to tell if a source is credible or not.
No matter your task at hand, having credible external links and/or citations is always preferred; but especially in writing SEO blogs. Type in your search term(s) plus .edu (or whatever type of website you want). These domain name extensions tend to have more authority than .com sites.
- Use .gov for official government websites.
- Use .edu for higher education websites.
- Use .org for organization websites. These are typically non-profit or educational organizations.
A word of caution, it’s always important to look for further details to determine a site’s credibility, such as an author name, a date of publication, a publisher, and other information.
Google Scholar
Whether you’re a current student or you just like learning, Google Scholar is a free tool for everyone to find and access academic journal articles and other publications. It’s a great way to weed out the “fluff” of regular internet content.
The main page takes you to a Google search homepage where you can choose the Articles or Case law tab. You can filter your results by date of publication or a custom date range, results with patents, and results with citations.
Google Scholar pulls from online books, scholarly journals, higher education publications, and more. Many of the sources are free and have open access, though some may require a login with a library subscription.
There is also a feature to star sources and build your own source library and a citation tool when you click the quotation mark symbol. The citation tool gives you citations in multiple styles, e.g. MLA, APA, and others.
Advanced Search
Advanced Search for websites
If you’re finding your Google SERP overloaded with content, the Advanced Search for websites is a great tool to refine your results. You can filter results by:
- Last update
- Site or domain
- Where search terms appear on the page
- File type
- Usage rights
Advanced Image Search features
You can also do an Advanced Image Search. This kind of search will help you find the perfect image to feature in your work with usage rights. You can filter results by:
- Image size
- Aspect ratio
- Image colors
- File type
- Type of usage rights
Google Books
Another type of source for research is print. Because printed materials have to go through an extensive publishing process, they are one of the most reliable source types.
Google Books has an archive of previews and fully scanned books and magazines. Publishers might upload books, while some are there because of the Library Project. Some books published before 1923 are automatically a part of the Public Domain and therefore available for free.
How to use Google Books:
1. Search the book title, ISBN number, or keywords
2. You can search with filters using the Google Books Advanced Search tool
3. Find a title
4. From there you can download, cite, or even translate the book. *Not all full texts are available for free, some may just offer a preview (which can still be useful!).
You can even save books and create your own Google books library and create “shelves” for different categories.
Why does Lifted Logic care about helping people use Google more efficiently?
To put it simply, we’re nerds in love with the web.
But seriously, we believe that understanding how to navigate internet search engines, whether you’re an everyday person or a business, is super important. Think about it!
People rely on searching the internet for stuff like:
- Deciding which college to attend
- Searching for a job
- Finding a place to live
- Growing a business
There are some serious life decisions that could potentially be determined by your ability to research on Google. You might as well learn the ins and outs so you don’t miss out on crucial information that could impact your life’s ~journey~.
In summary, we’ve covered:
- Common Google user errors and search tips
- SEO and SERP; what they are and why they’re important
- Google tools for research and how to use them
Have you been trying out an SEO campaign to grow the online presence of your business? Lifted Logic offers free SEO evaluation for your business so you can learn how to be even better.





